Managing multiple credit cards can be a strategic way to maximize rewards and benefits, but it also requires careful planning and organization to avoid pitfalls.
Few effective strategies to manage multiple credit cards wisely
1. Create a Card Usage Strategy
Assign specific purposes to each credit card based on their unique benefits. For example, use one card for grocery shopping that offers cash back in that category, while another card might provide travel rewards for flights and hotel bookings. This approach ensures you maximize the rewards from each card without overspending.
2. Set Up Automatic Payments
To avoid late fees and maintain a good credit score, set up automatic payments for at least the minimum due on each card. You can choose to pay the full balance or a fixed amount monthly. Automating payments helps ensure you never miss a due date, especially when juggling multiple cards.
3. Use a Budgeting App
Employ a budgeting app to track your spending across all credit cards. This can help you monitor balances, due dates, and overall spending patterns in one place, making it easier to manage your finances effectively.
4. Regularly Review Statements
Scrutinize your credit card statements each month to catch any unauthorized transactions or billing errors. This practice not only helps in identifying potential fraud but also allows you to stay on top of your spending and adjust your budget accordingly.
5. Monitor Annual Fees and Benefits
Keep track of the annual fees associated with each card and assess whether the benefits you receive justify these costs. If a card is too expensive relative to the rewards it offers, consider cancelling it to streamline your credit card portfolio.
6. Optimize Credit Utilization
Aim to keep your credit utilization ratio below 30% on each card to maintain a healthy credit score. This means spreading your expenses across multiple cards instead of maxing out one card. If necessary, consider transferring balances to lower your utilization on high-balance cards.
7. Set Spending Alerts
Most credit card issuers allow you to set up alerts for spending thresholds or upcoming due dates. Use these notifications to keep your spending in check and remind you of important payment deadlines.
8. Consider Balance Transfers
If you find yourself with high-interest debt on one card, look into balance transfer options. This allows you to move your unpaid balance to a card with a lower interest rate, giving you more time to pay off the debt without incurring high charges.
9. Limit the Number of Cards
While having multiple cards can provide benefits, it’s wise to limit the number of cards you actively use. Managing too many can become overwhelming and may lead to missed payments or increased fees. Focus on a few cards that best meet your needs and provide the most value.
10. Regularly Reassess Your Card Portfolio
As your financial situation and spending habits change, periodically review your credit card strategy. Ensure that the cards you hold still align with your current lifestyle and financial goals, and make adjustments as necessary.
Credit cards are a big part of financial life in India today. They make it easy to buy things, offer rewards, and provide flexibility in managing money. However, they also have some risks if not used carefully. Let’s break down the benefits and potential pitfalls with simple examples.
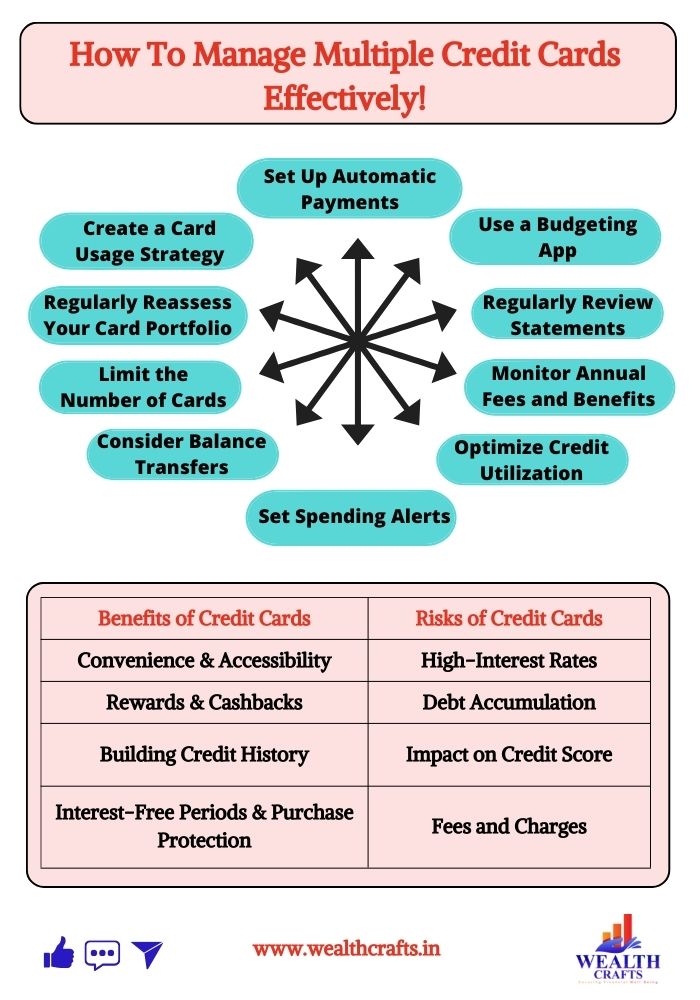
The Benefits of Credit Cards
Convenience and Accessibility
Credit cards offer a highly convenient and flexible method for making purchases, whether you’re shopping online or in a physical store. They streamline the buying process by allowing individuals to avoid carrying large sums of cash, which can be inconvenient and unsafe/risky. Instead, with a credit card, you have immediate access to a line of credit, making transactions smooth and efficient.
For instance, consider a scenario where you wish to buy a new smartphone priced at ₹ 30,000. If you don’t have that exact amount readily available in your bank account at the moment, a credit card can still make this purchase possible. You can then repay this amount over time, either in full by the end of the billing cycle to avoid interest charges or through monthly instalments, depending on your financial situation and the terms of your credit card agreement
Rewards and Cashbacks
Many credit cards come with attractive rewards programs designed to provide additional value and incentives to cardholders. These rewards can take various forms, such as cashback, travel points, or discounts on purchases. For example, a credit card might offer a cashback reward of 5% specifically on grocery purchases.
Let’s consider a scenario where you use this credit card for your monthly grocery shopping. If you spend ₹ 10,000 on groceries throughout the month, the 5% cashback reward means you would earn ₹ 500 in cashback. This cashback amount is essentially a discount on your spending, which can be credited back to your account or used towards future purchases, depending on the credit card’s policy.
Such rewards not only make everyday expenses more cost-effective but also provide an opportunity to save money or earn perks just by using the card for routine transactions. Over time, these rewards can accumulate and contribute significantly to your overall savings or enhance your purchasing power.
Building Credit History
Responsible credit card use, such as making timely payments, is essential for building a good credit history. Your credit history, a detailed record of how you manage credit, is a crucial factor in determining your creditworthiness. Lenders use this history to assess your ability to repay loans. A strong credit history can significantly enhance your financial opportunities, making it easier to secure loans for major purchases like home mortgages, car loans, and personal loans.
Interest-Free Periods
Credit cards typically offer an interest-free grace period of 15-45 days. This allows users to make purchases and defer payment without incurring interest, effectively borrowing money at no cost if the balance is paid in full by the due date.
Purchase Protection
Credit cards often come with added security features, such as fraud protection and the ability to dispute unauthorized charges. This can provide peace of mind when making significant purchases
The Risks of Credit Cards
High-Interest Rates:
One of the major risks associated with credit cards is their high-interest rates. The annual interest rate (AIR) can range from 24% to 40% in India.
Let’s say you have a credit card balance of ₹ 20,000 and your card’s annual interest rate (AIR) is 36%. This means that for every ₹ 100 you owe, you’ll be charged ₹ 36 in interest over a year.
Annual Interest Rate Calculation:
- Monthly interest rate: 36% annual interest rate / 12 months = 3% Per Month
- Monthly interest on ₹ 20,000: ₹ 20,000 * 3% = ₹ 600
- Annual interest: ₹600/month * 12 months = ₹ 7,200
The Impact of Carrying a Balance: If you only make the minimum payment each month, the interest will continue to accrue on the remaining balance. Over time, this can significantly increase your overall debt.
Debt Accumulation:
Credit cards can lead to debt accumulation if not managed responsibly. For example, if you use a credit card to spend ₹ 50,000 but only make the minimum payment of ₹ 1,000 per month, and not making the full payments, it can extend the repayment period significantly, resulting in substantial interest charges. This can create a cycle of debt that’s difficult to break out of.
Impact on Credit Score:
While credit cards can be instrumental in building a positive credit history, misusing them can have an impact on your credit score. Consistently missing payments, accumulating high balances, or exceeding credit limits can significantly lower your score, making it more challenging to secure loans or favorable interest rates in the future.
Fees and Charges:
Credit cards come with various fees that can add up if not managed carefully. Fe of the charges include:
| Fee’s/Charges | % Range / Flat Fee | Explanation |
| Annual Fee | 0% – 3% | Annual fee for using the credit card |
| Late Payment Fee | ₹100-₹1,000 | Charged when a payment is missed after the due date |
| Annual Interest Rate (AIR) | 24% – 49% per annum | Annual Interest Rate (AIR) applied to unpaid Amount |
| EMI Conversion Charges | 1%-2% | Fee for converting credit card purchases into EMIs (Equated Monthly Instalments) |
| ATM Withdrawal Fee | ₹300-₹500 per transaction | Fee for withdrawing cash from ATMs using a credit card |
| Card Replacement Fee | ₹100-₹250 | Fee for issuing a new/replacement card in case of loss or damage |
| Foreign Transaction Fee | 1%-3.5% | This fee is charged for converting the currency and processing the transaction internationally |
Note: The specific charges and percentages may vary depending on the credit card issuer and type. Check your card’s terms and conditions for accurate information.
Credit cards are indeed a double-edged sword. They offer significant advantages, including convenience, rewards, but they also come with potential downsides such as high-interest debt, various fees, and potential negative impacts on your credit score. To fully benefit from credit cards while minimizing these risks, it is essential to use them wisely. Regularly monitoring your credit card statements will help you maintain financial health and address any issues promptly. By adopting responsible credit card practices, you can enjoy the benefits while keeping your financial situation under control.
Want to manage your credit card use more effectively? Discover practical tips and strategies to optimize your credit card benefits and avoid common pitfalls. Schedule a free consultation call today to understand to understand how to get the most out of your credit cards.






