Throughout history, gold investment has stood as an asset prized not just for its brilliance but also for its enduring stability. This precious metal offers a unique set of benefits for investors, making it a compelling addition to any portfolio. In this blog, we will explore various aspects of gold investment, including insights into Sovereign Gold Bonds (SGBs), physical gold, Gold ETFs, Gold Mutual Funds, and Digital Gold. Additionally, we will delve into more detailed topics surrounding SGBs, such as redemption processes, taxation implications, and inherent limitations in this investment option
Why Investing in Gold Shines Bright!
Beyond its undeniable beauty, gold holds a timeless value that transcends market fluctuations. In periods of economic turmoil, when stocks and bonds can plunge, gold traditionally exhibits stability, acting as a haven for your investments. Adding gold to your portfolio diversifies your holdings, which can help mitigate risk. Since gold often moves in the opposite direction of stocks and bonds, its presence helps balance your portfolio’s overall performance.
Decoding Gold Investment: Exploring Physical Gold, Gold ETFs, Gold Mutual Funds, SGBs and Digital Options

Physical Gold –
Physical gold investment, in the form of bullion or coins, serves as a tangible asset with intrinsic value and a hedge against economic uncertainty. Unlike paper assets, physical gold offers investors a tangible means of preserving wealth and diversifying investment portfolios.
Exploring the Pros of physical gold ownership –
- Tangible Asset: Unlike stocks or bonds, physical gold is something you can hold in your hand. This tangibility can provide a sense of security for some investors.
Exploring the Cons of physical gold ownership –
- Storage Costs: Safeguarding physical gold can become a significant expense. Whether you opt for a bank’s safe deposit box or invest in a home safe, there are ongoing costs associated with securing your precious metal holdings.
- Security Risk: Physical gold is inherently attractive to thieves due to its high value. Without adequate security measures in place, there is a tangible risk of loss. Burglaries, robberies, or even accidental misplacement can lead to substantial financial setbacks
- Limited Liquidity: Liquidating physical gold assets may not be as swift or straightforward as selling stocks or bonds. Finding a buyer, verifying authenticity, and negotiating a fair price can all be time-consuming processes. Moreover, during times of market volatility, selling physical gold might necessitate settling for less than the spot price, further impacting your returns.
- Lack of Passive Income: Unlike many other investment options, physical gold does not offer any passive income streams. Unlike stocks that pay dividends or bonds that generate interest, owning gold bullion or coins does not provide ongoing cash flow. As a result, investors reliant on regular income may find physical gold less appealing compared to income-generating assets.
- Making Charge: Another consideration is the making charge, which adds to the cost of purchasing physical gold. This charge covers the cost of manufacturing the gold item and is typically non-recoverable when selling the gold.
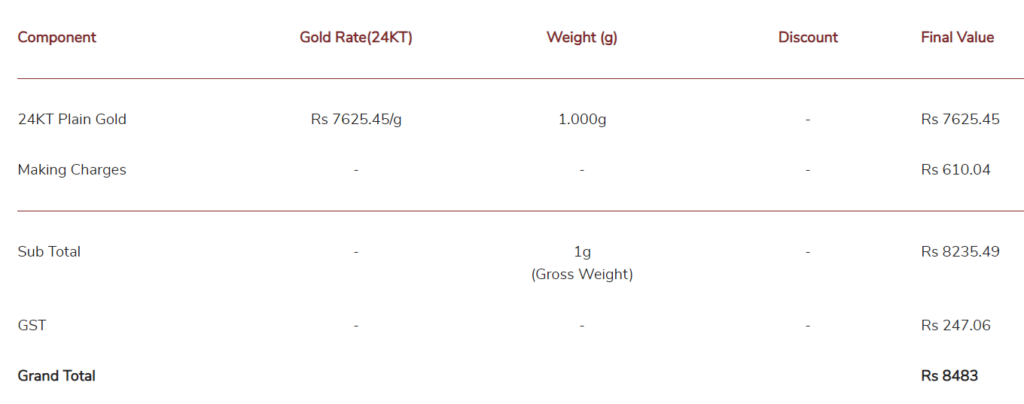
Above image is taken from Tanishq website – Gold Price as on 19/04/2024
Gold ETF’s
Gold ETFs are exchange-traded funds designed to mirror the domestic physical gold price. These passive gold investment instruments are based on gold prices and invest in gold bullion. Essentially, Gold ETFs represent physical gold in paper or dematerialized form.
Advantages
- Regulated by SEBI: Gold investment through ETFs are regulated by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), ensuring investor protection and adherence to regulatory standards.
- No GST: Unlike physical gold purchases, buying and selling Gold ETFs do not attract Goods and Services Tax (GST), reducing transaction costs for investors.
- No Lock-in Period: Investors in Gold ETFs enjoy the flexibility of buying and selling units at their convenience, without any lock-in period constraints, providing liquidity and ease of investment.
Disadvantages
- Taxable Capital Gains: Gains from trading Gold ETFs are subject to capital gains tax, potentially reducing overall returns for investors.
- Expenses Ratio: Gold ETFs typically incur expenses, with a minimum expense ratio of 0.1%, which can eat into investors’ profits over time.
- Limited Liquidity: Selling Gold ETFs may prove challenging due to lower liquidity compared to other assets, potentially resulting in delays or unfavourable sale prices for investors.
Gold Mutual Funds
Mutual Funds provide gold investment opportunity for individuals to gain exposure to the precious metal through professionally managed portfolios. These funds invest in a variety of gold-related assets, including gold mining companies, bullion, and exchange-traded funds (ETFs). By pooling resources from multiple investors, gold mutual funds provide diversification and potentially higher returns than individual investments.
Pros
- No Demat Account Required: Unlike investing directly in gold through ETFs or physical gold, gold mutual funds do not require investors to have a Demat account. This makes investing in gold more accessible to a broader range of investors who may not have Demat accounts or are unfamiliar with the process.
- Can Start with Minimum SIP of ₹ 100: Gold mutual funds offer the flexibility of starting with a minimum SIP (Systematic Investment Plan) investment of just ₹ 100. This low entry point allows even small investors to participate in the gold market systematically over time, enabling them to benefit from rupee cost averaging and accumulate gold holdings gradually.
Cons
- Expenses Ratio: Gold mutual funds typically have an expense ratio of at least 0.1%, which represents the annual fee charged by the fund for managing investors’ money. This expense can reduce the overall returns earned by investors over time.
- Market Volatility Risk: Gold prices can be subject to significant fluctuations due to various factors such as economic conditions, geopolitical events, and investor sentiment. As a result, investments in gold mutual funds are exposed to market volatility, and investors may experience fluctuations in the value of their investments.
Digital Gold
Digital gold investment presents a modern and convenient way for investors to access the gold market without the need for physical ownership. It allows individuals to purchase and own fractions of gold bullion electronically, typically through online platforms or mobile applications. Digital gold platforms often offer features such as easy accessibility, transparency, and flexibility in buying and selling gold in small denominations
Positives
- Fort Knox in Your Pocket: Unlike physical gold, where storage can be a concern, digital gold is held securely by the company. Say goodbye to safety deposit box fees and worries about theft!
- No Making Charges: Unlike physical gold, you do not incur any additional making charges when buying digital gold. You pay for the gold itself at the prevailing market rate.
- Flexibility for Physical Delivery (with charges): While digital gold offers easy storage, you can still opt for physical delivery if needed. However, there might be making charges and other fees associated with converting digital gold to physical form.
- No Minimum Investment Requirement: Investors can start with any amount they prefer, as there is no minimum investment threshold, providing accessibility to a wide range of investors.
Negatives
- Tax Time Trouble: While there is no need for physical storage, there is a cost for digital security. You will need to factor in a 3% GST (Goods and Services Tax) when you purchase digital gold, adding to the overall investment cost.
- Hidden Fees Lurk: Beyond the initial GST, there are often hidden costs associated with digital gold. These can include spreads of 3% to 6%, which encompass storage fees, insurance, and other maintenance charges. These fees eat into your potential profits.
- Selling Spread Squeeze: Hoping to cash in on your digital gold? Be prepared for another spread of 3% to 6% when you sell. This can significantly impact your returns, especially for short-term investments.
Apart from considering the positives and negatives, it is important to acknowledge the challenges associated with digital gold investments.
- Limited Holding Period: While some platforms offer flexibility, you may not be able to hold your digital gold indefinitely. Some companies may nudge you to sell or take physical delivery after a certain timeframe. This physical delivery comes with making charges, impacting your overall return.
- Unregulated Market: Currently, the digital gold market in India lacks established regulations. The three major players – MMTC (Government Owned), Safe Gold, and Augmont (Private) operate in a relatively unsupervised space. This underscores the importance of choosing a reputable and trustworthy provider with strong security measures.
- Tax Implications: Be sure to factor in capital gains tax when considering your digital gold investment strategy. The tax implications will depend on your holding period (short-term or long-term) and how you choose to exit your investment (selling digitally or taking physical delivery).
Now the question arises: Which is the best instrument for gold investment?
Sovereign Gold Bonds (SGBs) stand out as the premier choice for gold investment. SGBs offer security and credibility backed by the Government of India. They eliminate storage and security concerns associated with physical gold. With fixed interest payments, SGBs provide an additional source of income. Their liquidity allows easy buying and selling on stock exchanges. Moreover, SGBs offer tax benefits, with capital gains exempt from tax upon redemption after the maturity period. Overall
A Comprehensive Guide to Sovereign Gold Bonds (SGBs) Investment
Here are some key points of SGB’s
- Issued by: Reserve Bank of India (RBI) on behalf of the Government of India.
- Eligible Investors:
- Resident individuals
- Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs)
- Trusts
- Universities
- Charitable institutions
- Ineligible Investors:
- Non-resident Indians (NRIs)
- Overseas Citizen of India (OCI)
- Person of Indian Origin (PIO)
- Private limited companies
- Firms
- Limited Liability Partnerships (LLPs)
- Investment Limits
- Minimum: 1 gram of gold
- Maximum: 4 kilograms for individuals and HUFs & 20 kilograms for trusts, universities, and charitable institutions
- Purchase Modes:
- Cash (up to ₹20,000)
- Demand Draft (DD)
- Cheque
- Online payment
- Joint Ownership and Minors: Allowed (with a guardian’s help for minors)
- How can we Purchase:
- Authorized banks (nationalized, scheduled private, and scheduled foreign)
- Designated post offices
- Stock exchanges (through brokers)
- Stock Holding Corporation of India Limited (SHCIL)
- Benefits:
- 2.5% annual interest paid semi-annually
- Nomination facility available – Yes
- Holding Options:
- Demat form (electronic holdings)
- Certificate form (physical certificate)
Understanding Redemption and Payout in Sovereign Gold Bonds (SGBs)
- Sovereign Gold Bonds (SGBs) have an initial lock-in period of 8 years, during which investors cannot redeem their bonds. However, they have the option to extend this lock-in period for an additional 3 years if desired & Investors have the opportunity for an early exit from Sovereign Gold Bonds (SGBs) in the 5th, 6th, or 7th year. The selling price at redemption is determined by the closing average price of the gold over three days.
- Additionally, SGBs can be bought in the primary market and sold in the secondary market.
- Loans can be secured against Sovereign Gold Bonds (SGBs), providing investors with a valuable collateral option. Additionally, SGBs are eligible for gifting, but only to relatives, offering a means of transferring gold ownership within family circles.
- The price of gold is decided by the India Bullion and Jewellers Association (IBJA), but this price is not applicable in the secondary market & in the secondary market, the price of SGBs is determined by demand and supply and SGBs can be traded in demat format.
- Even if investors miss the initial issue date, they can still acquire Sovereign Gold Bonds (SGBs) later in the secondary market, ensuring continued access to this investment opportunity.
Demystifying Taxation on Sovereign Gold Bonds (SGBs)
- Interest earned on Sovereign Gold Bonds (SGBs) stands at 2.5% and is paid out semi-annually. This interest income is subject to taxation based on the individual’s applicable slab rates.
- Selling Sovereign Gold Bonds (SGBs) to the RBI or government upon maturity does not trigger tax liabilities. However, selling SGBs in the secondary market incurs capital gains tax, irrespective of maturity status. The tax rate varies based on the holding period, with short-term gains (held for under 3 years) taxed at regular slab rates, and long-term gains (held for more than 3 years) subject to long-term capital gains tax.
- Inheriting or receiving Sovereign Gold Bonds (SGBs) as gifts does not lead to any tax liabilities for the recipient.
Unveiling the Limitations: Navigating the Downsides of Sovereign Gold Bonds (SGBs)
- Lock-in Period: The primary drawback of SGBs is the long lock-in period of 8 years, with an optional extension of 3 years. This restricts your access to your invested capital for a significant timeframe.
- Early Redemption Penalty: While you can exit before maturity during the 5th, 6th, or 7th year, the redemption price is set by the government and may not reflect the current market value of gold. You could potentially lose out on any appreciation in gold price during that period.
- Limited Liquidity: Compared to physical gold or gold ETFs, SGBs held in certificate form have lower liquidity. Selling them before maturity in the secondary market might not be convenient and could lead to a price lower than the prevailing market rate due to demand and supply factors.
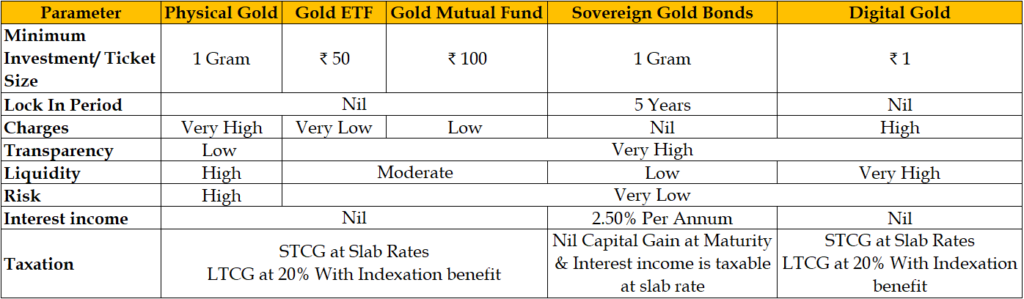
In conclusion, Sovereign Gold Bonds (SGBs) emerge as the optimal choice for investing in gold when compared to physical gold, Gold ETFs, Gold Mutual Funds, and digital gold investment options. SGBs offer a unique combination of benefits that make them stand out in the investment landscape.
Firstly, they provide the safety and security of owning gold without the hassle of physical storage or security concerns.
Secondly, SGBs offer interest payments, enhancing returns over time, unlike physical gold.
Thirdly, they are backed by the Government of India, ensuring credibility and trust.
Additionally, SGBs provide liquidity through listing on stock exchanges, allowing easy buying and selling. Unlike Gold ETFs and Mutual Funds, SGBs do not carry fund management charges, making them cost-effective. Moreover, SGBs offer tax benefits, exempting capital gains tax upon redemption after the maturity period. Lastly, in the era of digitalization, SGBs provide a seamless and convenient investment avenue. Although SGBs have some limitations, they still represent the best option compared to other gold investment alternatives.
Diversify your portfolios with a secure and transparent gold investment option! Sovereign Gold Bonds (SGBs) offer a government-backed alternative to physical gold investment, eliminating storage risks and associated costs. SGBs provide guaranteed principal protection based on gold price movement, attractive interest payments, and potential capital gains – all exempt from capital gains tax upon maturity. Expand your investment horizons and hedge against inflation with SGBs. Explore this timely opportunity and a free introductory call today to explore how we can work together to strengthen your expertise in this key investment area.



