Estate planning is an important process that helps you organize how your belongings and finances will be handled when you pass away. It’s not just about what happens to your money or property; it’s also about ensuring your wishes are followed, making things easier for your loved ones, and avoiding unnecessary legal troubles. In this blog, we’ll break down the key components of estate planning like wills, trusts, Powers of Attorney, Advance & Healthcare Directive etc.
Understanding Estate Planning
At its core, estate planning involves making thoughtful decisions about how your assets will be managed and distributed upon your death. It can also address important issues like healthcare decisions and guardianship for minor children. The overarching goal is to create a comprehensive plan that minimizes stress for your loved ones and maximizes the value of your estate, ensuring a smooth transition for all involved.
Key Components of Estate Planning
Will
A will is a legal document that explains how you want your wealth and money to be shared after you pass away. It lets you choose who will receive your property and can also name guardians for any children you have who are still minors. This way, you can make sure your wishes are followed and your loved ones are taken care of.
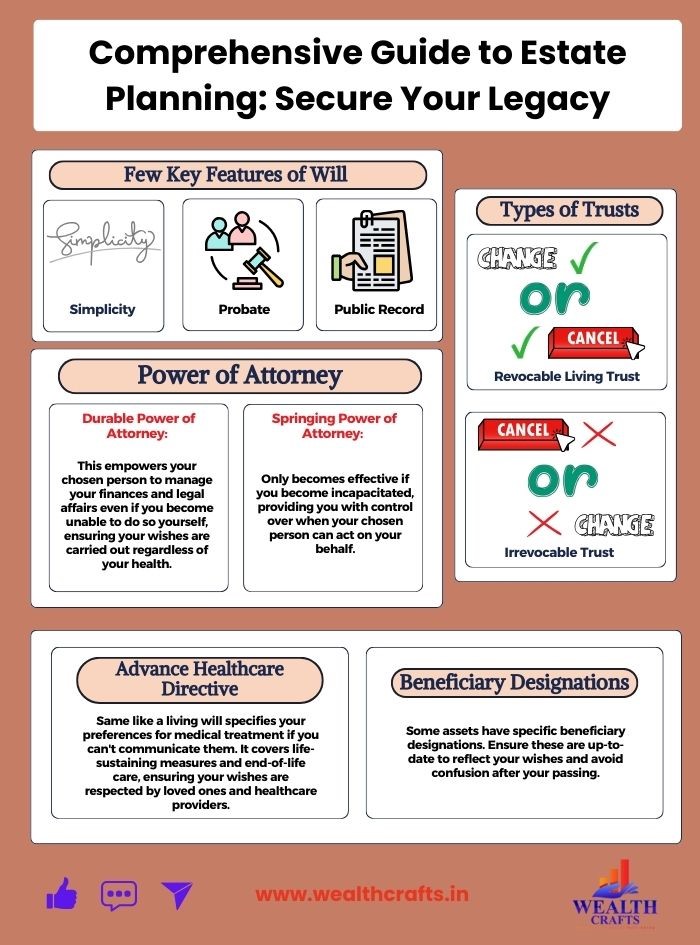
Key Features of a Will:
Simplicity: Wills are generally straightforward to create and can be easily updated whenever you need to make changes. This means that as your life circumstances change like getting married, having children, or acquiring new assets you can adjust your will to reflect your current wishes.
Probate: After you pass away, your will usually goes through a process called probate. This legal procedure ensures that the will is valid and helps manage the distribution of your assets according to your wishes. During probate, a court oversees everything, which can take some time but helps ensure that everything is handled fairly.
Public Record: Once a will has been probated, it becomes a public document. This means that anyone can access it, which can lead to a loss of privacy regarding your financial matters and personal wishes. While this transparency helps prevent fraud, it also means that details about your estate and beneficiaries may be available to the public.
Few Important Points to Consider
- If someone dies without a will, they are considered “intestate,” meaning there are no instructions for distributing their estate, which will be handled according to succession laws. For Hindus, this is governed by the Hindu Succession Act of 1956; Muslims are covered by the Muslim Succession Act of 1935; and Christians and Parsis follow the Indian Succession Act of 1925.
- Having a will is crucial to ensure your loved ones are not left in a difficult situation.
- It’s important to have a valid and up-to-date will that clearly outlines your wishes.
- If you have multiple wills, revoke all previous ones to prevent any conflicts.
- While registering a will isn’t mandatory, it’s advisable if you think it might be contested; you can register it with the sub-registrar.
- A registered will can be modified or revoked at any time, and any changes (called a codicil) must also be registered.
- Create an inventory of your assets and liabilities to keep track of everything.
- Appoint an executor or legal representative to carry out the instructions in your will.
Trusts
Trusts are more complex than wills and come with added advantages. They let you transfer your assets into a trust, which is then managed by a trustee on behalf of your beneficiaries. This means that instead of directly passing on your assets after your death, the trust can manage and distribute them according to your wishes while you’re still alive. Trusts can help avoid probate & provide privacy making them a useful tool for effective estate planning.
Types of Trusts:
- Revocable Living Trust: This type of trust allows you to keep control over your assets while you’re alive. You can change or cancel it whenever you want. After your death, the assets in the trust pass directly to your beneficiaries without going through probate, making the process quicker and more private.
- Irrevocable Trust: Once you create this trust, you can’t change or cancel it. It often provides benefits like tax savings and protection from creditors, as the assets are no longer considered part of your estate.
- Special Needs Trust: This trust is specifically designed for beneficiaries with special needs. It helps provide financial support without affecting their eligibility for government benefits, ensuring they receive the care they need without losing crucial assistance.
Powers of Attorney
A power of attorney (POA) is a legal document that gives someone else the authority to make financial or legal decisions for you. This can be especially important if you become unable to manage your affairs due to illness or injury. With a POA in place, your chosen representative can handle tasks like paying bills, managing investments, or making healthcare decisions, ensuring that your interests are protected even when you can’t speak for yourself.
Types of Power of Attorney:
- Durable Power of Attorney: This type remains effective even if you become incapacitated, allowing your chosen person to manage your financial and legal matters without interruption. It ensures that your affairs can be handled according to your wishes, no matter what happens to your health.
- Springing Power of Attorney: This type only takes effect under specific conditions, typically when you become incapacitated. This means your chosen person won’t have authority to act on your behalf until you are no longer able to make decisions for yourself, providing you with an added layer of control over when and how the authority is activated.
Advance Healthcare Directive
Also known as a living will, this document outlines your preferences for medical treatment if you are unable to communicate your wishes. It typically includes important decisions about life-sustaining measures, such as whether you want to be kept on life support, and details about your end-of-life care. Having a living will ensures that your healthcare providers and loved ones understand your wishes during a difficult time, helping to ease the burden on them and ensure your choices are respected.
Beneficiary Designations
Certain assets, such as life insurance policies and retirement accounts, let you name beneficiaries directly. This means that when you pass away, these assets will go to the people you designated, regardless of what your will says. Because of this, it’s important to keep these beneficiary designations current and accurate to ensure that your wishes are followed and your loved ones are taken care of. Regularly reviewing them can help prevent any confusion or disputes later on.
Additional Considerations in Estate Planning
- Tax Implications: Estate taxes can greatly impact your estate’s value. It’s essential to understand laws for effective planning.
- Digital Assets: Don’t forget to include digital assets in your estate plan, such as social media accounts, cryptocurrencies, and online bank accounts. Provide access information and specify how you want these assets to be managed.
- Regular Review and Update: Your estate plan should evolve with your life. Major events like marriage, divorce, the birth of children, or changes in financial circumstances should trigger a review of your plan.
- Communication: Discussing your estate plan with family members can prevent misunderstandings and conflicts. Open communication helps clarify your wishes and provides reassurance to your loved ones.
Getting Professional Help
While you can create a basic estate plan on your own, consulting with an estate planning lawyer can ensure that your documents comply with laws and truly reflect your wishes. They can also provide valuable insights on complex issues, such as tax implications and trust management.
Conclusion
Estate planning is an integral part of securing your legacy and protecting your loved ones. By understanding the components of estate planning – including wills, trusts, powers of attorney, and healthcare directives. you can create a comprehensive plan tailored to your unique situation. Remember to regularly review and update your estate plan to adapt to life changes. With careful planning, you can ensure that your wishes are honored and your family is cared for, even after you’re gone.
Ready to take control of your financial future and secure your legacy? Don’t leave your estate planning to chance! Schedule a free consultation call today. We’ll help you navigate the complexities of estate planning.



